Laboratory automation is a game-changer that revolutionizes the way tasks are done in a lab. By utilizing robots and advanced technologies, laboratories can streamline processes and achieve better accuracy, efficiency, and speed.
These robots come in various types, each with distinct advantages and limitations tailored to specific applications.
Here, we’ll explore the advantages and disadvantages of each robot type to help you understand how HF-i can help you achieve your laboratory automation objectives.
However, they may require more supervision and maintenance, have limited capabilities, and can pose ethical and legal issues. They need to operate at slower speeds when compared to caged industrial robots.
HF-i uses co-bots for collaborative tasks requiring manual dexterity, flexibility, or feedback.
The advantages of these robots include high precision, speed, and repeatability, and they can handle different types of samples with ease. Industrial versions are extremely reliable, although they may be more expensive, bulky, and difficult to program than other robots.
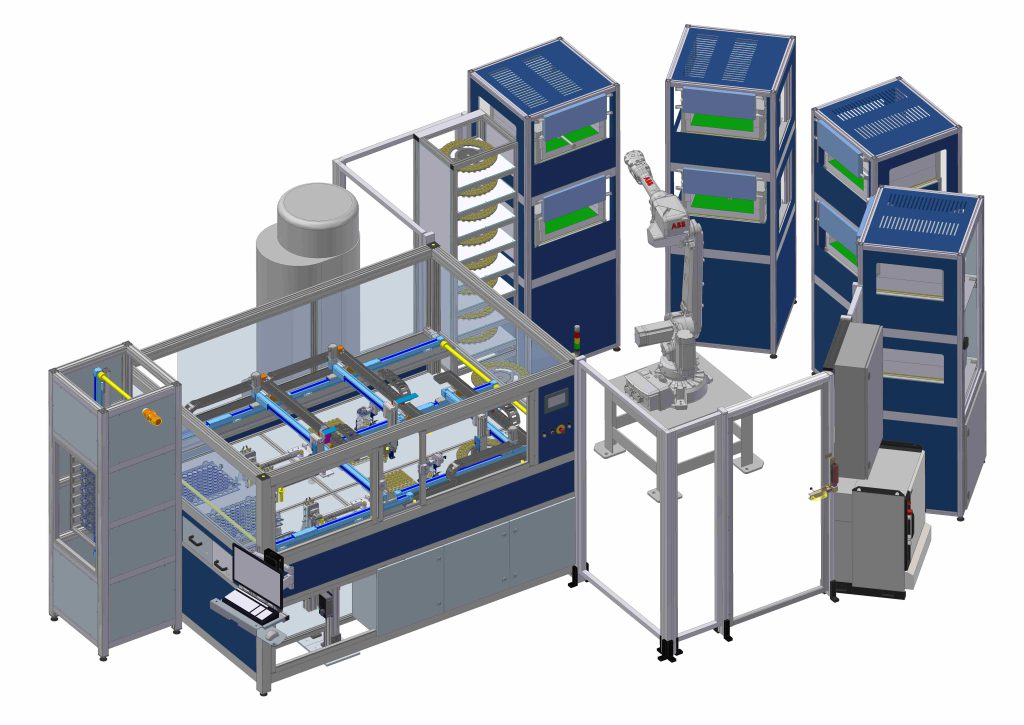
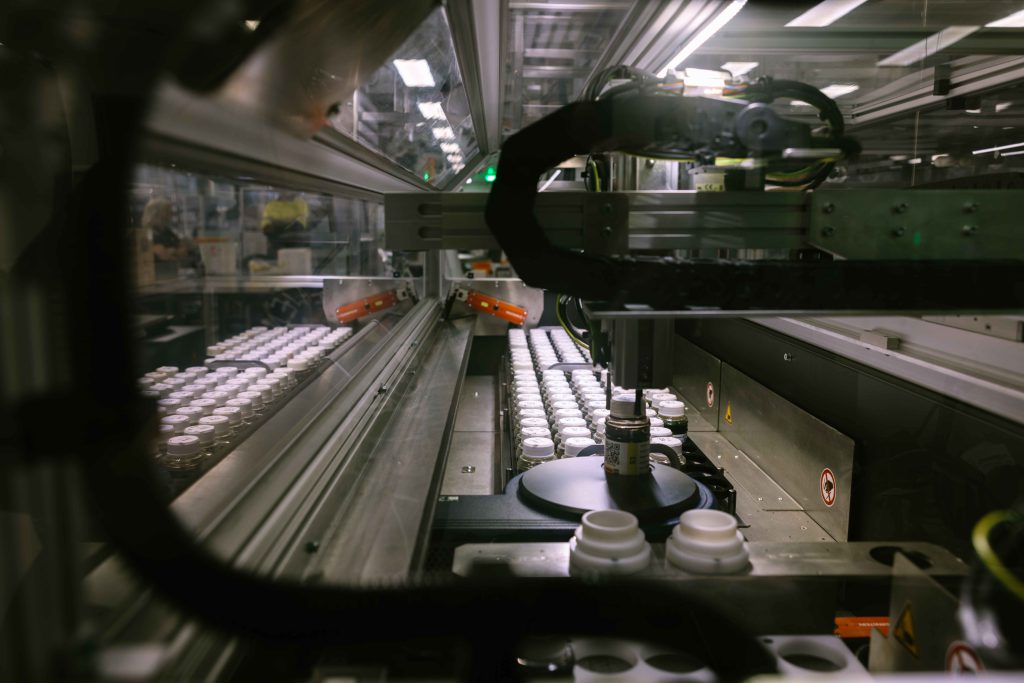
HF-i uses industrial-grade 6-axis robots to perform complex tasks that require high-speed movements, versatility, and precision, such as sample preparation, liquid handling, or instrument integration.
HF-i uses industrial-grade scara robots to perform simple tasks that require high speed and accuracy such as plate handling, dispensing, or sorting, where a larger surface area is required, and four degrees of freedom are sufficient.
HF-I uses industrial XYZ Cartesian robots to perform basic tasks that require low cost and high efficiency, high sample throughput such as pipetting, diluting, weighing, or washing.
HF-i uses large industrial gantry robots for handling sample storage, large numbers of samples in batches, and moving trays of samples between workstations.
HF-i uses industrial robots on tracks for handling heavy samples that need to move long distances between machines or where space and the number of connected machines require it.

HF-i combines different types of robots to create hybrid solutions that optimise laboratory automation. For example, a Cartesian robot (XYZ), a collaborative robot, and a Scara robot can be combined to perform high-precision and high-flexibility tasks safely and efficiently.
HF-i’s Approach: HF-i offers customized laboratory automation solutions by combining different types of robots tailored to each customer’s needs. These robots optimize sample handling, automate assays, and manage inventory.
HF-i also integrates other technologies such as vision systems, sensors, software, LIMS, and cloud computing to create smart and connected laboratory automation solutions. Customers can rely on HF-i’s expertise for efficient and reliable laboratory processes.